Are you concerned about your online privacy?
Today, due to the internet and computers, we can access and share information across the globe instantly. We can also connect with friends and family despite the distance between us.
But with such great capabilities, comes the privacy cost.
Whether you’re accessing or sharing information online, you risk losing your privacy.
The growing number of security breaches witnessed over the last decade has brought to people’s attention the need for healthy privacy habits.
According to Pew Research, 79% of Americans are concerned about the way their data is being used by companies and the government. Most also feel they have little control over how it’s used.
If you fall within this bracket of concerned citizens, it’s time to take control of your digital privacy and learn online privacy tips. Your best strategy is to learn to control how much trackable data you let out and who has access to your data.
This beginner’s guide to online privacy: 10 important tips, should get you started.
It’s the ultimate online privacy guide for complete amateurs.
1. Use Secure Operating Systems.
To start off with this online privacy guide, let’s look at the foundation. Ensuring your online privacy is founded on the operating system you use. It should be designed to offer privacy to its users.
Currently, the three most dominant operating systems across the world are macOS, Windows, and Linux. There’s a high chance you’re using one of these three.
So which is right and which is not?
Windows has the least privacy optimization. In fact, according to a study by BeyondTrust, Microsoft vulnerabilities increased by 48% in 2020 making it the least secure ecosystem.
In terms of privacy violations, your device is tagged with a unique advertising ID which helps advertising agencies offer personalized ads.

Secondly, data syncing (which is the synchronization of browsing history, Wi-Fi passwords, and setting across devices) is enabled by default.
Lastly, Microsoft can collect personal data and are at liberty to share it with third parties.
If this vexes you, then it’s time to switch to macOS or Linux. It’s certainly one of the best ways to protect your privacy online.
MacOS has a good reputation for sharing fewer user data and a more secure browser (Safari). Linux on the other hand has a list of distributions particularly designed for privacy.
The sudden shift of operating systems can feel uncomfortable at first but since you care about your privacy, it will be worth it.
2. Use Virtual Private Networks VPN
The internet is a global network of computers that have an Internet Protocol – IP addresses visible to any site that you visit. The site administrator can identify your device and know your location using this address.
In addition, your Internet Service Provider and other third parties can see the websites you visit and data you send or receive
Sadly, you cannot hide your IP address when accessing the internet. But you can pretend to have a different IP address and still access the internet with the help of VPNs.
According to SurfShark, 31% of the internet’s internet population use VPN.
The trend continues to grow as more people value privacy.

VPNs operate by extending a private network of computers across a public network and enable you to send and receive data across public networks as if the computers were directly connected to the private network.
When you surf with a VPN enabled, the VPN becomes your source of information and turns your data into gibberish through cryptographic encryption.
Even if someone was to get access to your data, they cannot decipher the data.
If every other tip in this list of online privacy tips seems unattainable, a VPN should serve your immediate privacy needs.
3. Use Privacy Enhanced Browser
A browser enables you to surf the internet. The software you’re using to read this article right now as a browser.
It collects data from an internet-connected server and renders it on your device in an organized format for you to interact with the data.
While interacting with other computers, a browser can expose some information about itself to any site it visits. This data, together with a combination of your browser settings can create a unique device fingerprint that makes you identifiable.
To circumvent this challenge, here is a guide to online privacy in two options;

First, use a browser with enhanced privacy settings. The Tor Browser comes with advanced privacy encryption and settings out of the box. It’s an indispensable tool if you want to know how to protect your digital privacy.
Epic Privacy Browser comes with VPN-like functionality that keeps you anonymous and protects your data from third-party access.
The second option is to configure your browser for enhanced privacy. Firefox Browser can achieve considerable privacy with a little tweaking of the default configuration and installation of privacy add-ons.
Brave Browser comes with automatic blocking of ads and trackers making your navigation smoother and safer.
4. Limit or Disable Internet Cookies
What is a cookie exactly?
An internet cookie is a file stored on your device that consists of website data sent by a website on your first visit. Cookies enable a website to identify returning visitors by checking past activity on the website to provide a personalized experience.
Cookies were created to improve the users’ experiences. However, cookies can be tracked across several websites by third parties and used to create browsing history profiles for targeted advertising.
In addition, a hacker in control of a malicious website can send malware cookies to your device, access your personal information and use it to impersonate you on another website.

If you don’t like the idea of cookies tracking your data, you have several options.
First, you can completely disable cookies on your web browser. But you’ll have to contend with poor browsing experiences, especially if you have poor internet connections.
Secondly, you can use private browsing which ensures cookies are cleaned after browsing, or manually clear cookies after every session.
Lastly, you can limit cookies to ‘first party’, allowing only the current site to write cookies.
Those are the best online privacy safety tips regarding cookies.
5. Use Websites with HTTPS Encryption
The internet uses protocols to transfer data across computers.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP is the basic communication protocol that was used for some time before Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) was introduced.
The difference between the two protocols is this; HTTP sends your data in plain text while HTTPS adds an encryption layer on your data.
For instance, if you use an HTTP website to send messages or emails, an attacker who’s suitably positioned in the network can eavesdrop and look at your data.

However, with HTTPS enabled, an attacker cannot decipher the encrypted data. HTTPS offers authentication through the certificate authoring system and assures the integrity and confidentiality of your data.
To identify a secure website, check the address or web page link in the search bar above the page. The links should start with https://
There goes another of the best online security tips.
If you’re using a smartphone, some browsers hide the extension for aesthetic purposes. Look for a green padlock sign to identify a secure website.
When browsing any site without HTTPS security, be sure not to share personal information as your information will be at risk of third-party access.
6. Use Up-to-date Antivirus Software
Antivirus software was originally created to detect and remove viruses. With time, they developed into full-blown security tools for computers and devices.
Besides eliminating malware, most modern antivirus software includes some element of privacy protection that prevents you from accessing malware-infected websites.
According to Kaspersky, 1 in every 5 internet users has been a victim of a malware attack at least once in their lifetime.
With so many types of apps used by our devices when connecting to the internet, it can be difficult to keep track of what’s installed on your device.

Bad actors can use sophisticated programs and sometimes software engineering to install malware and bloatware in your device that compromise your privacy and security.
So here’s a guide to online privacy.
To stay on top of your internet privacy game, you should invest in up-to-date and robust Antivirus software that can take care of your security and privacy needs.
Every day hackers are finding vulnerabilities in systems and using them to invade people’s computers for malicious intent.
Updated antivirus software comes with the latest malware prevention technology that is a step ahead of hackers.
7. Use Private Email Providers
Personal email services are free at surface value. But what most people don’t know is that the big, highly financed corporations behind these free services get a lot of value from your email data.
It’s not free. In exchange for the free service they provide, you give them exclusive access to your data.
Google, Yahoo, and Outlook command a large percentage of the email market. Allow me to use Google as an example considering that Google maintains a 92.47 % of search engine market share as per Statista,
When you log into your Gmail using a browser, Google begins to link your searches with your email address.
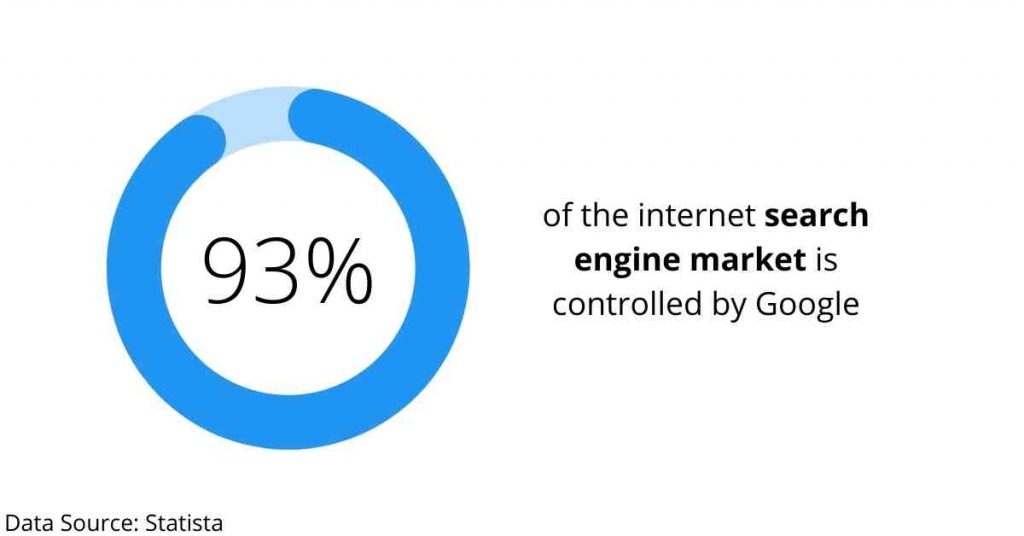
This linkage adds an extra identifiable data point to your web searches. In short, Google can identify you based on your search history.
If you don’t like the sound of that and want to know how to protect your digital privacy, consider switching to private messaging providers such as Proton Mail and Zoho Mail.
Proton Mail is a secure email provider designed to provide the best security and privacy features and does not have access to your information. Zoho Mail is equally optimized for your privacy.
8. Use Complex Unique Passwords
Am I right to assume that you use the same password for almost every application or website you use?
It makes sense because it’s easier to remember a password than to keep track of several passwords and where to use them. But that’s a mistake every online privacy guide will warn you against.
According to the Psychology of Passwords 2020 report by LastPass, 91% of people say they know reusing the same password or a variation of it is a risk and 66% of them admitted to doing it anyway.
Most internet users are more concerned about remembering their passwords than the security of their data.

To be safe, use complex unique passwords. For a start, avoid using variations of your personal information such as name, birthdate and phone numbers to create your passwords.
Any hacker with access to your computer can or social media platforms can easily acquire this data and try to crack into your accounts.
Instead, use indiscernible combinations of words, numbers, and characters to form your password. And since it’s best to have multiple passwords, use a password manager such as 1Password to keep track of all passcodes.
A great password is one of the best ways to protect your privacy online.
9. Avoid Public Wi-Fi Connections
Many times, internet users fall victim to malicious hacks and data breaches due to ignorance.
They’re only concerned about accessing the internet wherever, for free if possible. Hence we regularly log into public Wi-Fi hotspots oblivious of the underlying security threat to our personal data.
For instance, a survey by Decision Data found that 82% of people connect to any free Wi-Fi available in a public place. When asked about the security implications of their actions, most said they were not concerned about it.
Data sent through public Wi-Fi can be easily intercepted by bad actors in the network especially if your device is not well secured by an effective antivirus.

To ensure personal data security avoid using public Wi-Fi hotspots unless your device is well protected. It’s one of the best online privacy safety tips you can come around
Use smartphones instead of laptops, especially when managing sensitive information such as ecommerce, e-banking, and social media data.
Assume every public Wi-Fi hotspot is insecure and take precautions. Try to verify the legitimacy of the Wi-Fi connection by speaking to an employee in the location to give you legitimate access point information.
10. Limit Personal Information Sharing
The internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. Social media platforms for instance have taken center stage as we strive to stay connected with others,
However, corporations use this data to profile us for targeted advertising and bad actors can launch successful attacks on us based on this information.
Cambridge Analytica collected data of 87 million Facebook users and utilized it for political advertising which influenced elections in several countries including USA and Kenya.
If you’re fond of publishing very personal data such as where you live, pictures of your family, and your daily activities, you give hackers an easy time invading your privacy.
Be cautious with how much information you share online.
In addition, make use of privacy settings on social networks to control who sees what you post.
Remember also that once you post any information online, it will be hard to completely erase it. Friends who see this data can keep a copy especially if it has incriminating data.
Ultimately, assume everything you do online is not a profile and ensure you keep personal information private. That’s one of the best online security tips you’ll ever get.
Conclusion
The 10 tips you’ve just picked from the ultimate online privacy guide above are quite straightforward to implement.
Depending on your level of concern for your privacy, you can implement a couple of the tips or all of them. At the very least, have smart privacy habits and use security software to protect your data from unauthorized access.
Knowing that whatever you do online is not private will condition you to avoid sharing sensitive information online and remind you to use secure channels to share personal information.
Lastly, remember, the less information you have online, the more privacy you can enjoy.


