How do the most common VPN protocols work?
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide privacy for internet users. By creating secure tunnels and transporting encrypted data through them, they ensure you can surf the internet privately.
Lately, VPN usage has skyrocketed as concerns for online privacy continue to increase. According to Business Wire, VPN usage grew to a high of 27.1% in 2020 and the VPN market is projected to reach $107.5 Billion by 2027.
If you’re concerned about your privacy, investing in a good VPN is essential.
But how really do VPNs work?
What protocols do they use and how do they compare?
Some protocols are more secure than others but have compromised on speed. Others are more robust than others but compromise on privacy.
Understanding these VPN connection protocols can help you choose a VPN based on its qualities and limitations.
In this article, we’ll have 5 common VPN connection protocols explained and compared
1. PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is one of the oldest widely-used VPN remote access protocols. It was developed by Microsoft for dial-up connections and integrated with early Windows operating systems.
It encloses traffic data in a set of codes and routes it through an unsecured internet connection.
Using PPTP, TCP/IP traffic can be tunneled through the internet which helps remote users securely access local area networks using the internet.
PPTP revolves around Microsoft remote access service (RAS) which allows a network administrator to set up a client-server with a modem as a dial-in point for remote users.
The client-server authenticates the RAS users and sets up a network session using the Point-to-Point Protocol.
All protocols supported by remote access service i.e TCP/IP, NetBEUI, and IPX/SPX, are transported through the PPP connection.

Meanwhile, users see no difference between RAS through direct dial-in and RAS through the internet, while they enjoy the convenience of connecting to a RAS server from anywhere.
Besides convenience, PPTP is compatible with any device that uses Windows, macOS, and Linux. This means the installation of PPTP and configuration in most devices is easy.
And since it doesn’t require the installation of computer certificates or public key infrastructure to access, it is much easier to use.
However, the most significant challenge of PPTP is its low-security standards as compared to other protocols as it is limited to 128-bit encryption.
Thus challenge makes it the least secure protocol in VPN protocols comparison.
In addition, it is unreliable because you cannot determine whether the data sent is authentic or verify its origin.
For these security reasons, internet service providers often block PPTP protocols.
2. L2TP/IPSec
L2TP stands for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol. It was developed as a joint project between Microsoft and Cisco to support VPN connections.
The protocol was inspired by features from Microsoft’s PPTP protocol and Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding protocol, which were combined to provide more reliable and more secure VPN remote access protocols.
It starts by finding an IPSec association between two devices on a network.
Then, through the establishment of the Encapsulating Security Payload, a secure channel between a VPN client and a VPN server is set up.
L2TP comes into action by initiating a connection between its two endpoints; LAC (L2TP Access Concentrator) and LNS (L2TP Network Server). It first establishes and encapsulates a PPP link layer and transports it through the web.
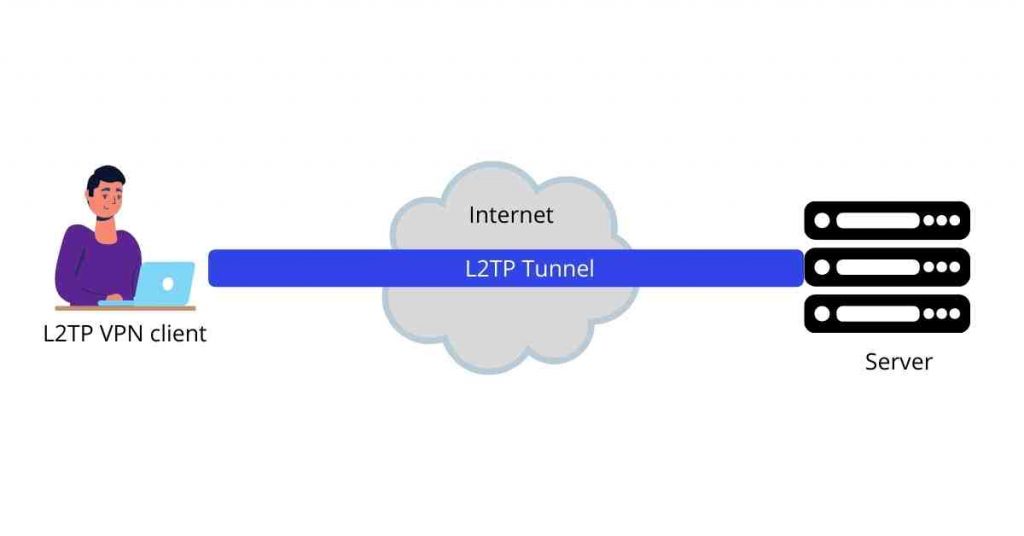
PPP connection is initiated in your device through your Internet Service provider before LAC accepts the connection. Then a free slot within the network is assigned and the request is passed on to LNS to complete the connection.
A virtual PPP connection is created to enable link frames to be passed freely through the tunnel.
The LNS accepts the frames, removes the encapsulation, and processes them as regular frames.
When L2TP is paired with IPSec, it uses powerful encryption ciphers and double encapsulation to secure data within a VPN.
Hence, it offers greater security and is more reliable than PPTP when you have the two top VPN protocols explained and compared.
However, in recent years advanced cyber experts have been able to bypass L2TP encryption. Hence, when dealing with very sensitive information, you should use a VPN provider with a more secure protocol and no-log policies.
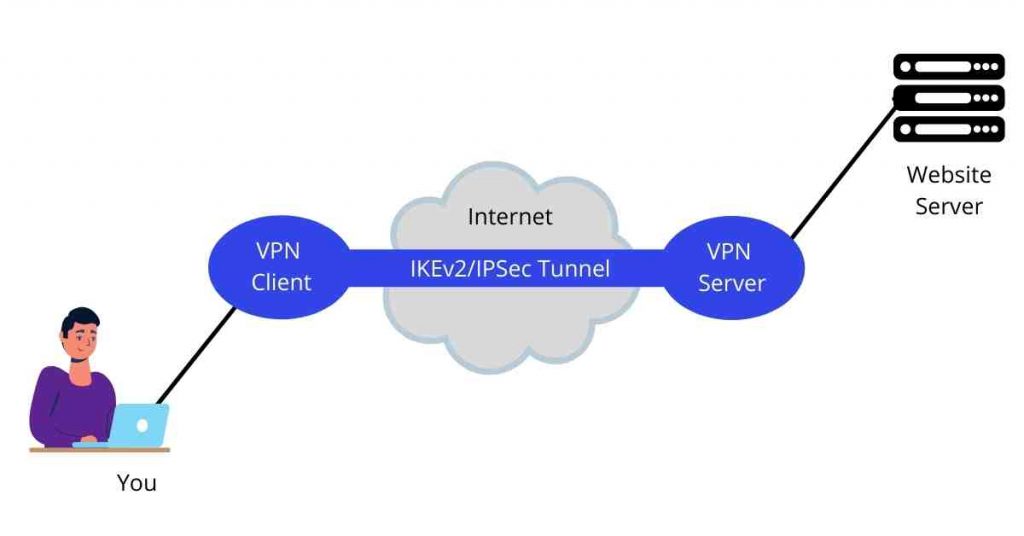
3. IKEv2/IPSec
IKEv2 refers to Internet Key Exchange version 2. It is a joint project between Microsoft and Cisco. Meanwhile, IPSec stands for Internet Protocol Security suite; a set of rules used to secure internet protocol.
Together, they form one of the most secure and widely used VPN protocols.
IKEv2 is responsible for generating encryption keys that ensure safe data flow between your device and the VPN server you’re connected to. It, therefore, creates a secure tunnel for data travel.
The protocol first authenticates the user’s device and the server. It then takes all the data – IP addresses, security measures used and ports utilized – and gives it to IPSec which encrypts it using the security associations.
After encryption, it uses tunnel mode – a secure enclosed connection between two devices using the internet – to send data.
IKEv2/IPSec uses a Diffie-Hellman key exchange which ensures perfect forward secrecy and supports fast VPN connections.
It offers robust security as it is compatible with other encryption ciphers including the popular AES 256 bit.
It offers high-speed data transfers making your VPN browsing experience faster and more enjoyable. Besides, if your internet connection is interrupted, it has a reconnect function to get you back online.
You can also switch between internet connections without losing your protection which makes it one of the most convenient VPN authentication protocols.
On the flip side, IKEv2 has several limitations. IKEv2 packets can become quite large which results in fragmentation occurring at the network layer which many firewalls and network devices are configured to block.
In addition, IKEv2 uses UDP ports 500 and 4500 for communication, which is often blocked by network administrators to prevent users from bypassing security controls.
4. WireGuard
WireGuard is a modern internet communication protocol that implements encryption in virtual private networks. It was developed by Jason Donenfeld originally for Linux but is now available in all top operating systems.
As an open-source protocol with significantly simpler code, it only requires a few thousand lines of code to develop as compared to other protocols.
I believe it’s the best VPN connection protocol in the market currently.
WireGuard uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to transmit encrypted IP packets using a port selected from its high ports range.
It then combines specific public keys with a list of allowed IPs and performs cryptokey routing in passing the packets through the VPN tunnel.
The public keys are unique for each peer and are used to authenticate the peers to each other. It also creates a single entry for an interface with which several peers are associated.
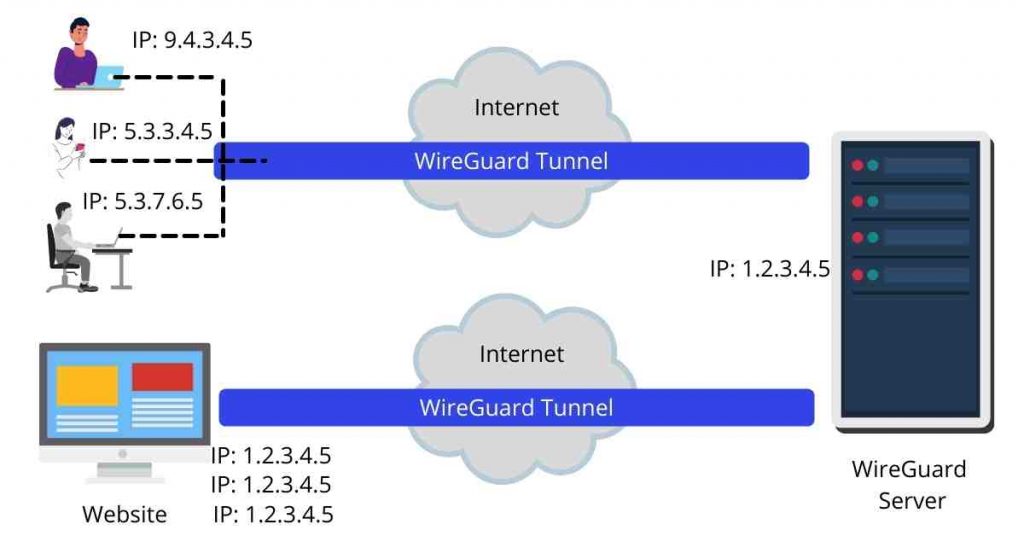
To encrypt a packet, WireGuard checks which peer it corresponds with. If the peer associated with the IP address is not identifiable, the packet is removed. If the peer is assigned successfully, it is encrypted with its public key.
WireGuard checks for the endpoint associated with the client and forwards the encrypted packet there.
To decrypt, it applies the same principles of associating peers with packets before decryption and only accepts a plaintext packet if the endpoint peer is allowed to receive packets from the initial endpoint.
Due to clean code configurations, WireGuard is much quicker and easier to set up. It was developed with new state-of-the-art cryptography making it one of the most secure VPN authentication protocols available.
On the flip side, WireGuard’s most significant limitation which is its major downside in VPN protocols comparison is that it compromises your privacy since it cannot be used without logging due to how it establishes connections.
5. OpenVPN
OpenVPN is a VPN protocol that secures point-to-point and site-to-site connections on the internet. It is an open-source application that was developed and released in 2001 by James Yonan.
It is currently one of the most popular VPN protocols.
Its widely used method of encrypting data and securing transmission over the internet makes it another best VPN connection protocol in the market.
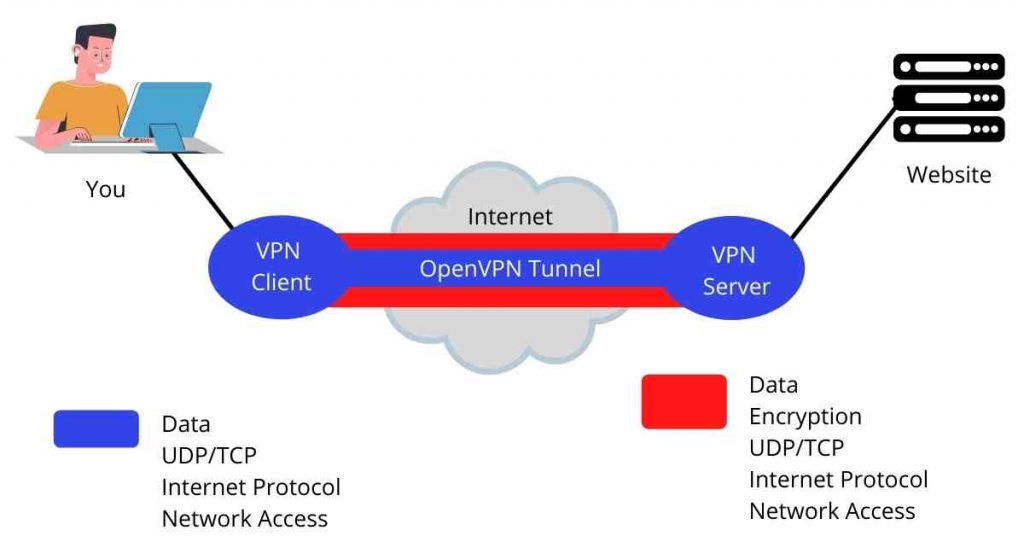
The OpenVPN protocol handles client-server communications by establishing a secure tunnel between the VPN client and the VPN server.
It uses the OpenSSL library to handle encryption and authentication. It starts by establishing a UDP connection which is faster but if it’s not possible, it uses a TCP connection which is more reliable.
Connection is composed of two levels; the client first connects with the server-side then connects with the internet.
Once the connection is established, the client appears as the server itself and the location of the server is identified as the IP origin.
Meanwhile, the identity and location of the client are kept secret.
The most significant advantage of OpenVPN is that it uses a good number of encryption techniques and algorithms, therefore, providing an advanced level of online protection.
Since it’s an open-source protocol, it’s more trustworthy as security experts can check the code itself and ensure things are working well.
However, due to high-end encryption methods of data encapsulation, it does not provide the best possible web connections as compared to PPTP and IKEv2. This is not to suggest you cannot have a great browsing experience; well-coded VPNs still provide decent internet speeds.
In addition, OpenVPN requires complex manual configurations which can be challenging for those who want to set up on their own.
Conclusion
We’ve just had top VPN protocols explained and compared
All the most popular VPN protocols we’ve discussed above have their own advantages and disadvantages.
However, the core lesson you can pick from this guide is that earlier protocols have become less secure and are slowly phasing out.
When selecting a good VPN, consider picking software that uses the latest protocols especially when sending highly sensitive information.
While most will be secure enough for normal internet activities, old protocols will not offer the best security considering the many forms of malware discovered regularly.
Additionally, pay attention to the limitations of each of the common VPN connection protocols explained and compared to ensure you select a VPN that serves your specific needs.


